MySQL to Redis Real-Time Sync

 TapData Cloud offers you cloud services that are suitable for scenarios requiring rapid deployment and low initial investment, helping you focus more on business development rather than infrastructure management. Free trial with TapData Cloud.
TapData Cloud offers you cloud services that are suitable for scenarios requiring rapid deployment and low initial investment, helping you focus more on business development rather than infrastructure management. Free trial with TapData Cloud. TapData Enterprise can be deployed in your local data center, making it suitable for scenarios with strict requirements on data sensitivity or network isolation. It can serve to build real-time data warehouses, enable real-time data exchange, data migration, and more.
TapData Enterprise can be deployed in your local data center, making it suitable for scenarios with strict requirements on data sensitivity or network isolation. It can serve to build real-time data warehouses, enable real-time data exchange, data migration, and more. TapData Community is an open-source data integration platform that provides basic data synchronization and transformation capabilities. This helps you quickly explore and implement data integration projects. As your project or business grows, you can seamlessly upgrade to TapData Cloud or TapData Enterprise to access more advanced features and service support.
TapData Community is an open-source data integration platform that provides basic data synchronization and transformation capabilities. This helps you quickly explore and implement data integration projects. As your project or business grows, you can seamlessly upgrade to TapData Cloud or TapData Enterprise to access more advanced features and service support.Redis is an in-memory key-value database, suitable for scenarios such as data caching, event publishing/subscribing, and high-speed queues. TapData allows you to sync data from relational databases (Oracle, MySQL, MongoDB, PostgreSQL, SQL Server) to Redis in real-time, helping you complete data flows quickly.
This article explains how to sync data from MySQL to Redis using a data transformation task.
If you need to sync a table from the source MySQL to Redis at the same time, you can create a data replication task. The setup process is similar to this article.
Prerequisites
Before creating a data transformation task, make sure you have set up the relevant data sources:
Procedure
Based on the product type, select the operation entry:
- TapData Cloud: In the left navigation panel, click Data Transformation.
- TapData Enterprise: In the left navigation panel, choose Data Pipelines > Transforms.
Click Create on the right side of the page.
On the left side of the page, drag both the MySQL and Redis data sources to the right side canvas, then connect them.
Click on the MySQL data source, and complete the configuration on the right panel according to the instructions below.
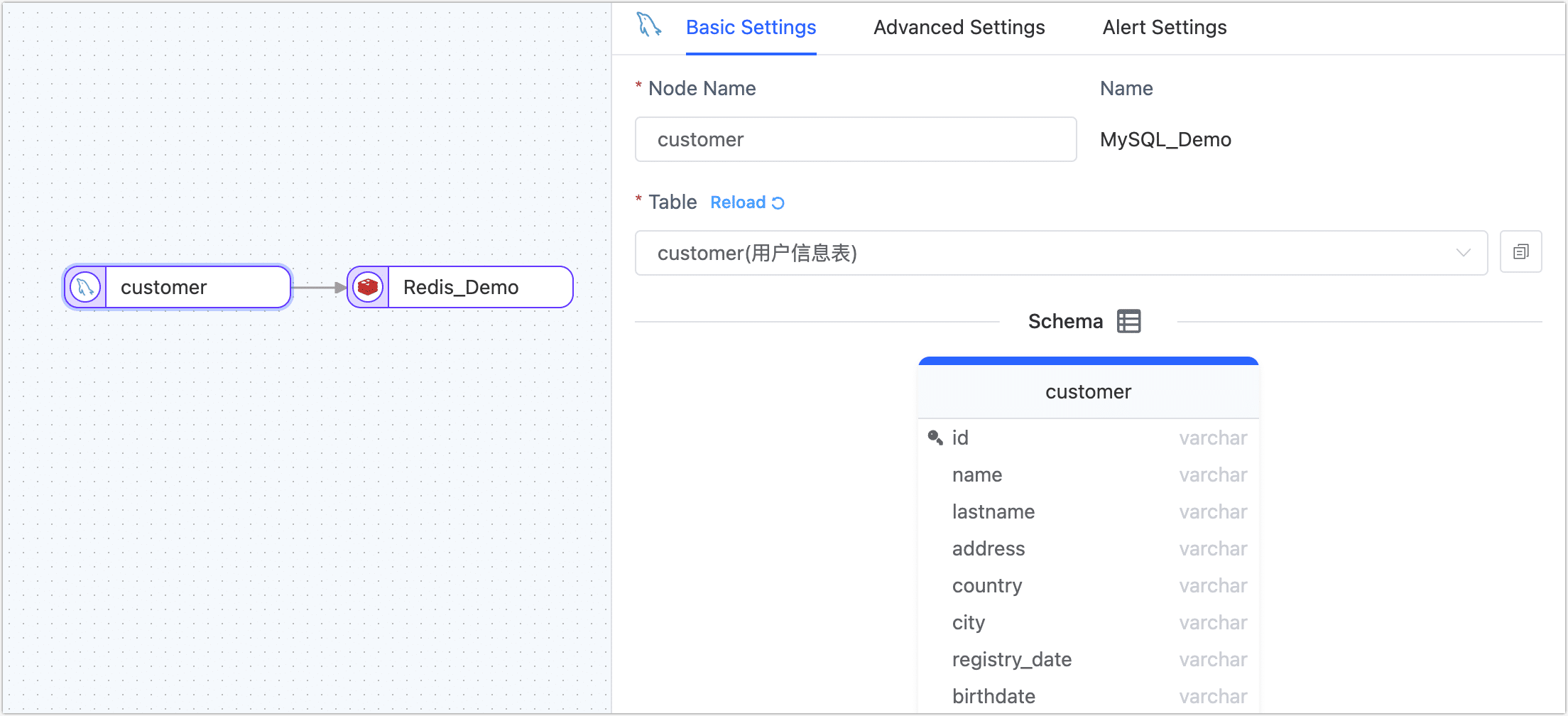
- Basic Settings
- Node Name: By default, it's the connection name, but you can also set a meaningful business name.
- Table: Select the source table to operate. The table structure, including column names and types, will be displayed below.
- Advanced Settings
DDL Synchronization
Choose whether to enable DDL Event Collection. When this switch is on, TapData will automatically collect the DDL events (like adding fields) from the selected source. If the target side supports DDL writing, the DDL statements can be synchronized.Incremental Method
Choose Log CDC or Polling. If you select Polling, you'll also need to specify the polling field, interval, and number of rows read each time.Log CDC will use the data source's transaction log to parse and sync incremental events. Polling will sync incremental events by polling a field, but it often can't sync delete events.
Data Filter
- Fully Customizable Query: Turn this on to input a custom SQL query for full data sync (doesn't affect the incremental stage). For example,
SELECT id,name,address FROM customer;.tipTo use this feature, the target node must be a weak Scheme type of data source (like MongoDB/Kafka) etc.
- Filter Settings: Off by default. Turn it on to specify data filtering conditions.
- Fully Customizable Query: Turn this on to input a custom SQL query for full data sync (doesn't affect the incremental stage). For example,
Batch Read Number: For full data sync, the number of records read per batch. Default is 100.
- Alert Setting
By default, if the node's average processing time is continuously 5 seconds or more for 1 minute, a system and email notification will be sent. You can adjust the rules based on your business needs or turn off the alerts.
- Basic Settings
Click on the Redis data source and complete the right panel's configuration according to the instructions below.
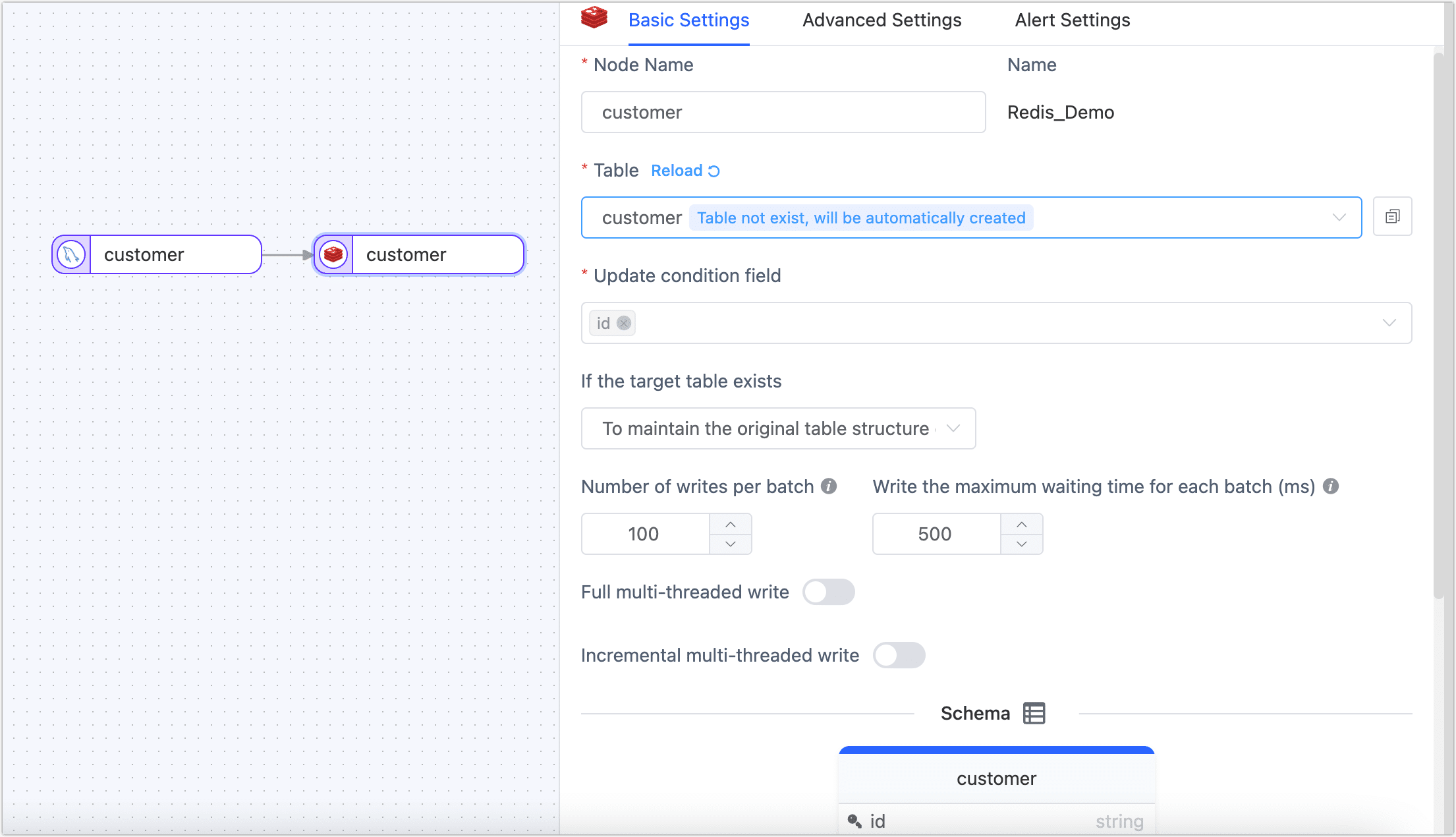
- Basic Settings
- Node Name: By default, it's the connection name, but you can also set a meaningful business name.
- Table: Choose the table where the processed data will be written to. If the specified table doesn't exist, it will be automatically created.
- Update Condition Field: Choose the field on which the update condition is based.
- Existing Data Handling: Depending on your business needs, choose the suitable option. If the target table has no data and its structure is different from the source table, you might want to choose Clear the Original Table Structure and Data on the Target Side.
- Number of Write Per Batch: During full data sync, the number of entries written per batch.
- Write the Maximum Waiting Time for Each Batch: Based on the performance of the target database and network latency, set the maximum wait time in milliseconds.
- Full Multi-Threaded Write: The number of concurrent threads for full data writing. The default is 8. Adjust based on the write performance of the target side.
- Incremental Multi-Threaded Write: The number of concurrent threads for incremental data writing. It's off by default. When turned on, adjust based on the write performance of the target side.
- Schema: Displays the table's structure, including field names and types.
- Advanced Settings
Data Writing Mode: Choose the data writing mode based on your business needs:
- Process by Event Type: After selecting this, you also need to choose the data writing strategy for insert, update, and delete events.
- Append Only: Only processes insert events, discards updates and delete events.
Data Source Specific Configuration
Storage Format: Supports the following three formats.
- String: The key-value is stored in a flattened way, meaning the key-value is stored as a single string.
- Hash: The key is a primary key, and the value is stored as a hash.
- List: The key is a primary key, and the value is stored as a list, with each entry containing a timestamp and value.
Save in One Key: When the storage format is set to List or Hash, this option can be set. Please be aware not to exceed the size limit for a single key in Redis (512 MB).
Include Head: When the storage format is set to List or Hash and Single Key Storage is chosen, turning on this switch will add a Hash key in Redis (default name is
-schema-key-). The value of this key is used to store the source table's name and column information, as shown below:HGETALL -schema-key-
1) "customer"
2) "id,name,lastname,address,country,city,registry_date,birthdate,email,phone_number,locale"Key Expression: The expression for the key name, formatted as
prefix_${column_name}_suffix. For example:db0_${id}_202301. The key name will bedb0_value of the id column_202301.Value Display: Supports the following two display methods.
- Json: Converts each record into a Json string.
- Text: Combines the corresponding values in the order of the fields with a specific delimiter. If the content contains this character, it wraps the content with escape characters.
- Alert Setting: By default, if the node's average processing time is continuously 5 seconds or more for 1 minute, a system and email notification will be sent. You can adjust the rules based on your business needs or turn off the alerts.
- Basic Settings
(Optional) Click on the settings icon in the top right corner of the page to configure task properties.
- Task Name: Enter a name that has business significance.
- Sync Type: You can choose both full and incremental, or you can select either full or incremental separately. 'Full' means copying the existing data from the source to the target, while 'incremental' means copying new or changed data produced by the source in real-time. Combining the two can be used for real-time data synchronization scenarios.
- Advanced Settings: Set the task's start time, incremental data processing mode, the number of processing threads, Agent, etc.
Once everything is confirmed to be correct, click Start.
After the operation is completed, you can observe the task's execution on the current page, such as RPS (Records Per Second), latency, task time statistics, and other information.
Result Verification
Based on the task settings, TapData will sync data from the customer table in source MySQL to Redis in real-time, storing it as a string type.
In MySQL, we randomly query a record with id 879f660510764c4ea4127447e7ca44b8:
mysql> select * from customer where id='879f660510764c4ea4127447e7ca44b8' \G;
... (rest of the content)
Then in Redis, we query the corresponding data:
127.0.0.1:6379> get db0_879f660510764c4ea4127447e7ca44b8_202301
... (rest of the content)
Task Management
On the task list page, you can start/stop, monitor, edit, copy, reset, delete, etc. tasks.
For detailed operations, refer to Manage Tasks.