Kafka-Enhanced

 TapData Cloud offers you cloud services that are suitable for scenarios requiring rapid deployment and low initial investment, helping you focus more on business development rather than infrastructure management. Free trial with TapData Cloud.
TapData Cloud offers you cloud services that are suitable for scenarios requiring rapid deployment and low initial investment, helping you focus more on business development rather than infrastructure management. Free trial with TapData Cloud. TapData Enterprise can be deployed in your local data center, making it suitable for scenarios with strict requirements on data sensitivity or network isolation. It can serve to build real-time data warehouses, enable real-time data exchange, data migration, and more.
TapData Enterprise can be deployed in your local data center, making it suitable for scenarios with strict requirements on data sensitivity or network isolation. It can serve to build real-time data warehouses, enable real-time data exchange, data migration, and more. TapData Community is an open-source data integration platform that provides basic data synchronization and transformation capabilities. This helps you quickly explore and implement data integration projects. As your project or business grows, you can seamlessly upgrade to TapData Cloud or TapData Enterprise to access more advanced features and service support.
TapData Community is an open-source data integration platform that provides basic data synchronization and transformation capabilities. This helps you quickly explore and implement data integration projects. As your project or business grows, you can seamlessly upgrade to TapData Cloud or TapData Enterprise to access more advanced features and service support.Apache Kafka is a distributed data streaming platform that allows real-time publishing, subscribing, storing, and processing of data streams. Kafka-Enhanced is an upgraded version of the Kafka connector, supporting both standard event structures and native Kafka data structures for data transmission. It removes the limitation of the previous Kafka connector, which only supported JSON Object formats, allowing non-JSON Object structures to be loaded into applications for processing. It also provides a more reliable resume-from-breakpoint mechanism.
This article explains how to add a Kafka-Enhanced data source in TapData, allowing it to be used as a source or target for building real-time data pipelines, such as for real-time data warehouses.
Kafka-Enhanced has been supported since version 3.15.
Supported Versions and Architectures
- Versions: Kafka 2.0 ~ 2.5 (built on Scala 2.12)
- Architectures: Single-node or cluster
Supported Data Types
| Category | Data Types |
|---|---|
| Boolean | BOOLEAN |
| Integer | SHORT, INTEGER, LONG |
| Floating Point | FLOAT, DOUBLE |
| Numeric | NUMBER |
| String | CHAR (supported as a source), VARCHAR, STRING, TEXT |
| Binary | BINARY |
| Composite | ARRAY, MAP, OBJECT (supported as a source) |
| Date/Time | TIME, DATE, DATETIME, TIMESTAMP |
| UUID | UUID (supported as a source) |
Consumption Details
When configuring data replication or transformation tasks later, you can specify the data synchronization method through task settings in the upper-right corner. The corresponding consumption details are as follows:
- Full Only: Reads from the first message and stops the task after reaching the recorded incremental position.
- Full + Incremental: Reads from the first message to the recorded position and then continuously syncs incremental data.
- Incremental Only: Choose the starting point for incremental collection as Now, meaning sync starts from the current position, or Select Time, meaning sync starts from the calculated position based on the specified time.
Since Kafka as a message queue only supports append operations, avoid duplicate data in the target system due to repeated consumption from the source.
Limitations
- Data Type Adaptation: As a source, Kafka's data types need to be adjusted according to the target data source's requirements, or corresponding table structures should be manually created on the target side to ensure compatibility.
- Message Delivery Guarantee: Due to Kafka's
At least oncedelivery semantics and append-only behavior, duplicate consumption may occur. Idempotency must be ensured on the target side to avoid duplicate data resulting from repeated consumption. - Consumption Mode Limitation: Consumption threads use different consumer group numbers, so be aware of the impact on consumption concurrency.
- Security Authentication Limitation: Currently, only authentication-free Kafka instances are supported.
Connect Kafka-Enhanced
In the left navigation bar, click Connections.
On the right side of the page, click Create.
On the redirected page, search for and select Kafka-Enhanced.
Complete the data source configuration as described below.
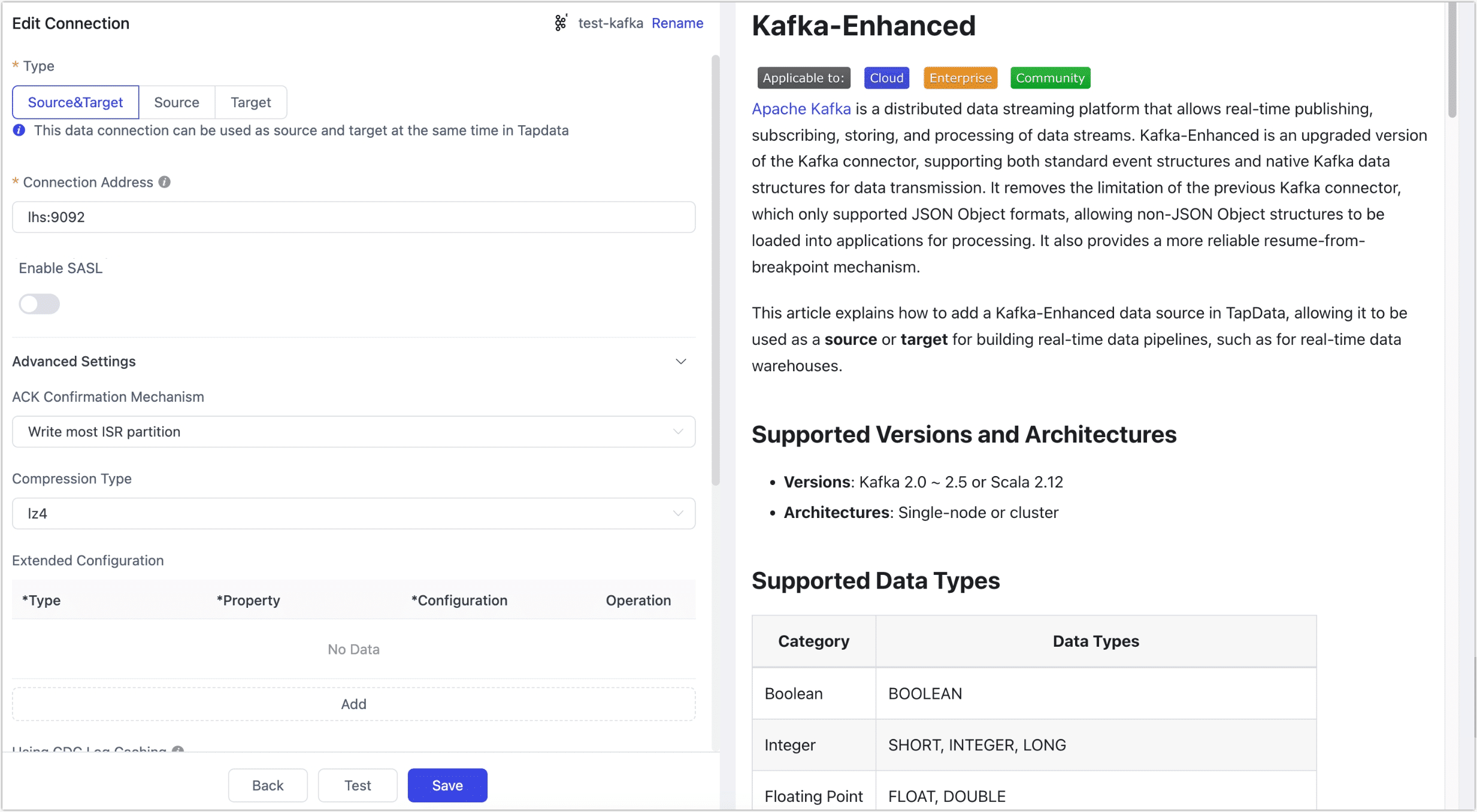
- Connection Settings
- Name: Enter a meaningful and unique name.
- Type: Supports using Kafka-Enhanced as a source or target database.
- Connection Address: Kafka connection address, including address and port, separated by a colon (
:), for example,113.222.22.***:9092. - Enable SASL: Whether to enable SASL (Simple Authentication and Security Layer) authentication for Kafka. If enabled, you’ll need to configure the username, password, and SASL mechanism (e.g.,
SCRAM-SHA-512).
- Advanced Settings
- ACK Confirmation Mechanism: Choose based on business needs: No confirmation, write to Master partition only, write most ISR partitions (default), or write to all ISR partitions.
- Compression Type: Supports lz4 (default), gzip, snappy, zstd. Enable compression for large messages to improve transmission efficiency.
- Extended Configuration: Supports custom advanced connection properties for Kafka managers, producers, and consumers for optimization in specific scenarios.
- CDC Log Caching: Mining the source database's incremental logs. This allows multiple tasks to share the same source database’s incremental log mining process, reducing duplicate reads and minimizing the impact of incremental synchronization on the source database. After enabling this feature, you will need to select an external storage to store the incremental log information.
- Include Tables: The default option is All, which includes all tables. Alternatively, you can select Custom and manually specify the desired topics by separating their names with commas (,).
- Exclude Tables: Once the switch is enabled, you have the option to specify topics to be excluded. You can do this by listing the table names separated by commas (,) in case there are multiple topics to be excluded.
- Agent settings: Defaults to Platform automatic allocation, you can also manually specify an agent.
- Model Load Time: If there are less than 10,000 models in the data source, their schema will be updated every hour. But if the number of models exceeds 10,000, the refresh will take place daily at the time you have specified.
- Connection Settings
Click Test, and after passing the test, click Save.
tipIf the connection test fails, follow the instructions on the page to resolve the issue.
Advanced Node Features
When configuring data replication or transformation tasks, and using Kafka-Enhanced as either a ource or target node, TapData provides additional advanced features to maximize performance and meet business needs:
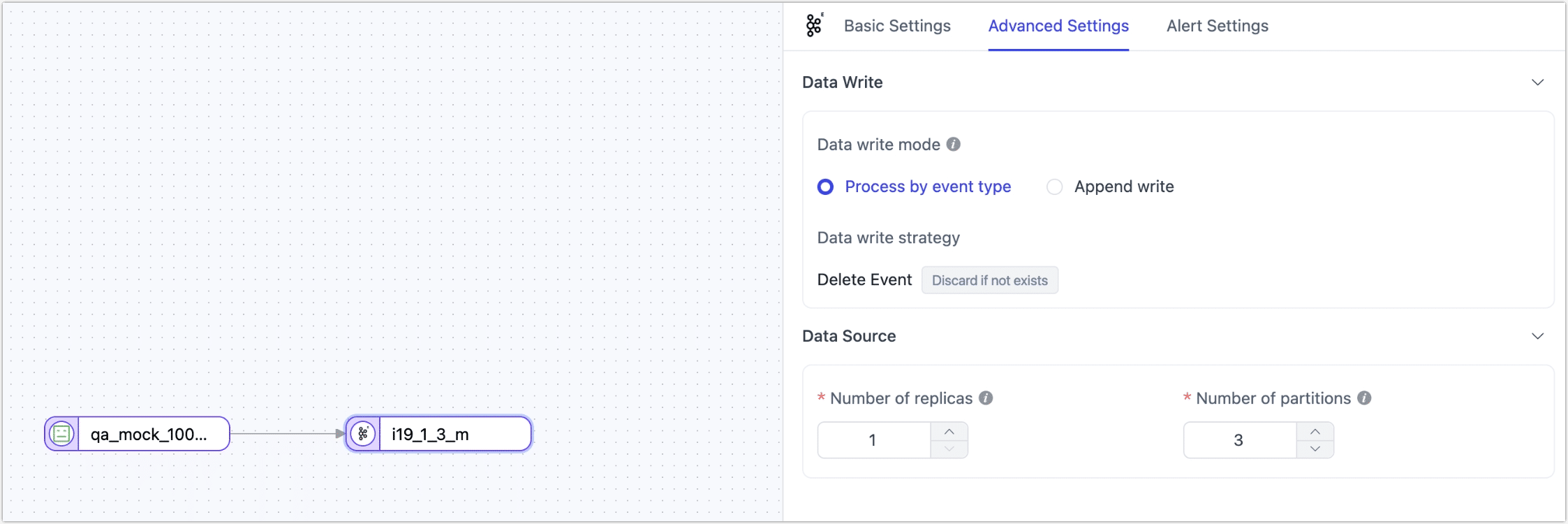
As a source node
Max Read Concurrency: Default is
1, meaning single-threaded reading. When set greater than1and the number of topics + partitions is greater than1, it will take effect with the smaller of the two values.As a target node
- Target Topic: Specifies the Kafka topic to which data will be written. Supports dynamic naming using placeholders such as
{db_name},{schema_name}, and{table_name}to auto-generate topic names based on database and table. - Number of Replicas: Default is
1, used when creating topics. Does not take effect if the topic already exists. - Number of Partitions: Default is
3, used when creating topics. If the configuration is greater than the number of partitions for the corresponding topic, it will automatically expand the partitions. - Structural mode: You can choose the data format for writing to the target based on your business requirements.
- Target Topic: Specifies the Kafka topic to which data will be written. Supports dynamic naming using placeholders such as
- Standard Structure (Default)
- Original Structure
- Canal
- Debezium
- Flink CDC
Description: Supports synchronization of complete DML operations (INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE). As a source, it parses and restores DML + DDL events for downstream processing; as a target, it stores these events in a standardized format, facilitating future task parsing.
Typical Use Case: In the CDC Log Queue, use the "Standard Structure" to write relational data change events from MySQL into Kafka, and then consume the data to write it into other databases.
Sample Data:
{
"ts": 1727097087513,
"op": "DML:UPDATE",
"opTs": 1727097087512,
"namespaces": [],
"table": "table_name",
"before": {},
"after": {},
}
Field Descriptions:
- ts: The timestamp when the event was parsed, recording the time the event was processed.
- op: Event type, indicating the specific operation, such as
DML:INSERT,DML:UPDATE,DML:DELETE. - opTs: Event timestamp, indicating when the data change actually occurred.
- namespaces: A collection of schema names for multi-schema scenarios.
- table: The table name indicating where the data change occurred.
- before: Data content before the change, available only for
UPDATEandDELETEoperations. - after: Data content after the change, applicable to
INSERTandUPDATEoperations.
Description: Uses Kafka's native data synchronization method, supporting append-only operations similar to INSERT. As a source, it handles complex, unstructured data and passes it downstream; as a target, it allows flexible control over partitions, headers, keys, and values, enabling custom data insertion.
Typical Use Case: Used for homogeneous data migration or unstructured data transformation, enabling data filtering and transformation through a Kafka -> JS Processing Node -> Kafka/MySQL data pipeline.
Sample Data:
{
"offset": 12345,
"timestampType": "LogAppendTime",
"partition": 3,
"timestamp": 1638349200000,
"headers": {
"headerKey1": "headerValue1",
},
"key": "user123",
"value": {
"id": 1,
"name": "John Doe",
"action": "login",
"timestamp": "2021-12-01T10:00:00Z"
}
}
Field Descriptions:
- offset: Offset marking the message position, not included in the target message body.
- timestampType: Type of timestamp, used for metadata purposes, not included in the message body.
- partition: Specifies the partition number for message writing, written to the specified partition if provided.
- timestamp: Message creation time, uses the specified time if provided, otherwise uses the system time.
- headers: Message header information, written to the header if present, carrying additional metadata.
- key: Message key, used for partitioning strategies or to identify the message source.
- value: Message content, containing the actual business data.
Description: Compatible with the open-source Canal format. Supports detailed MySQL type information and structural changes (DDL/DML). During data synchronization, it carries full database type, field info, and metadata—ideal for integration with the Canal ecosystem or scenarios where original MySQL data fidelity is required.
Typical Use Case: Suitable for consuming Canal-format data in real-time big data pipelines, such as Kafka → Hudi or Spark Streaming.
Sample Data:
{
"data": [
{
"id": "1",
"name": "Jack",
"age": "25",
"update_time": "2023-10-01 12:00:00"
}
],
"database": "test_db",
"es": 1696156800000,
"id": 123456,
"isDdl": false,
"mysqlType": {
"id": "int(11)",
"name": "varchar(255)",
"age": "int(11)",
"update_time": "datetime"
},
"old": [
{
"age": "24"
}
],
"pkNames": ["id"],
"sql": "",
"table": "user",
"ts": 1696156800123,
"type": "UPDATE"
}
Field Descriptions:
- data: Array of updated rows, showing post-change values.
- database: Name of the database where the change occurred.
- es: Event timestamp (in milliseconds).
- id: Unique event ID for tracking.
- isDdl: Indicates whether the event is a DDL operation.
- mysqlType: MySQL-specific type definitions for each field.
- old: Array of pre-change values for updated fields.
- pkNames: List of primary key fields.
- sql: SQL statement that triggered the change (if applicable).
- table: Table name.
- ts: Event timestamp (in milliseconds).
- type: Type of change event (e.g., INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE).
Description: Compatible with the open-source Debezium format. Retains complete schema definitions, and binlog metadata from the source database—ideal for scenarios requiring transactional integrity and schema auditing.
Typical Use Case: Suitable for data auditing, real-time validation, cross-system synchronization, and quality control scenarios where schema and transactional accuracy are critical.
Sample Data:
{
"before": {
"id": 1,
"name": "Jack",
"age": 24,
"update_time": "2023-10-01 12:00:00"
},
"after": {
"id": 1,
"name": "Jack",
"age": 25,
"update_time": "2023-10-01 12:00:00"
},
"source": {
"version": "2.3.0",
"connector": "mysql",
"name": "dbserver1",
"ts_ms": 1696156800123,
"snapshot": "false",
"db": "test_db",
"table": "user",
"server_id": 223344,
"file": "mysql-bin.000001",
"pos": 12345
},
"op": "u",
"ts_ms": 1696156800123
}
Field Descriptions:
- before: Pre-change data. Present for UPDATE and DELETE events.
- after: Post-change data. Present for INSERT and UPDATE events.
- source: Metadata from the source system:
- version: Debezium version
- connector: Connector type (e.g., "mysql")
- name: Logical server name
- ts_ms: Timestamp in milliseconds
- snapshot: Indicates if the event is from a snapshot
- db: Database name
- table: Table name
- server_id: MySQL server ID
- file: Binlog file name
- pos: Position in the binlog
- op: Operation type — c (create), u (update), d (delete)
- ts_ms: Event timestamp in milliseconds
Description: Compatible with the lightweight change data structure from the Flink CDC project. It uses intuitive operator symbols to represent change types, supports seamless integration with the Flink ecosystem, and can be directly consumed in Flink SQL or streaming jobs.
Typical Use Case: Commonly used for connecting Kafka data sources to Flink streaming jobs, such as real-time dimension table updates, live analytics, and metrics computation.
Sample Data:
{
"data": {
"order_id": 1,
"quantity": 10
},
"op": "-U"
}
Field Descriptions:
- data: The record payload, containing all field values.
- op: Operation type, represented using simplified symbols:
- +I: Insert
- -U: Before update
- +U: After update
- -D: Delete