Monitor Data Synchronization with Heartbeat Tables

 TapData Cloud offers you cloud services that are suitable for scenarios requiring rapid deployment and low initial investment, helping you focus more on business development rather than infrastructure management. Free trial with TapData Cloud.
TapData Cloud offers you cloud services that are suitable for scenarios requiring rapid deployment and low initial investment, helping you focus more on business development rather than infrastructure management. Free trial with TapData Cloud. TapData Enterprise can be deployed in your local data center, making it suitable for scenarios with strict requirements on data sensitivity or network isolation. It can serve to build real-time data warehouses, enable real-time data exchange, data migration, and more.
TapData Enterprise can be deployed in your local data center, making it suitable for scenarios with strict requirements on data sensitivity or network isolation. It can serve to build real-time data warehouses, enable real-time data exchange, data migration, and more. TapData Community is an open-source data integration platform that provides basic data synchronization and transformation capabilities. This helps you quickly explore and implement data integration projects. As your project or business grows, you can seamlessly upgrade to TapData Cloud or TapData Enterprise to access more advanced features and service support.
TapData Community is an open-source data integration platform that provides basic data synchronization and transformation capabilities. This helps you quickly explore and implement data integration projects. As your project or business grows, you can seamlessly upgrade to TapData Cloud or TapData Enterprise to access more advanced features and service support.TapData uses heartbeat tables to write timestamp information to the source database every 10 seconds. By checking the timestamp information in the heartbeat tables, we can quickly determine the activity and health of the data source, thereby better monitoring the data synchronization path and ensuring the stability and reliability of the data synchronization path.
Applicable Scenarios
If the source database often has long periods without DML operations (such as data insertion), and you need to quickly determine the status of incremental tasks through the Incremental Checkpoint in the Task List to ensure the link status and incremental log acquisition are normal.
If the source database has many DML operations, it is necessary to prevent the incremental logs recorded by TapData from being archived and deleted, which would make it impossible to obtain the incremental checkpoint.
Considerations
- Since the heartbeat table function needs to automatically create the table and update the timestamp in the source database, ensure the database account has the necessary permissions before enabling. For example, in MySQL, ensure the account has CREATE, INSERT, and UPDATE permissions. For more on permissions, see Data Source Preparation.
- The heartbeat table is named _tapdata_heartbeat_table. Ensure the integrity and reliability of the heartbeat table data and avoid operations on it in the source database (such as deleting the table).
Enabling Heartbeat Tables for a Data Source
In the left navigation bar, click Connection Management.
Find the created data source and click Edit in the Actions column.
If setting this up during the creation of a new data source, the method is the same. For more information, see Connecting Data Sources.
Scroll down to the bottom of the page and turn on the heartbeat table switch.
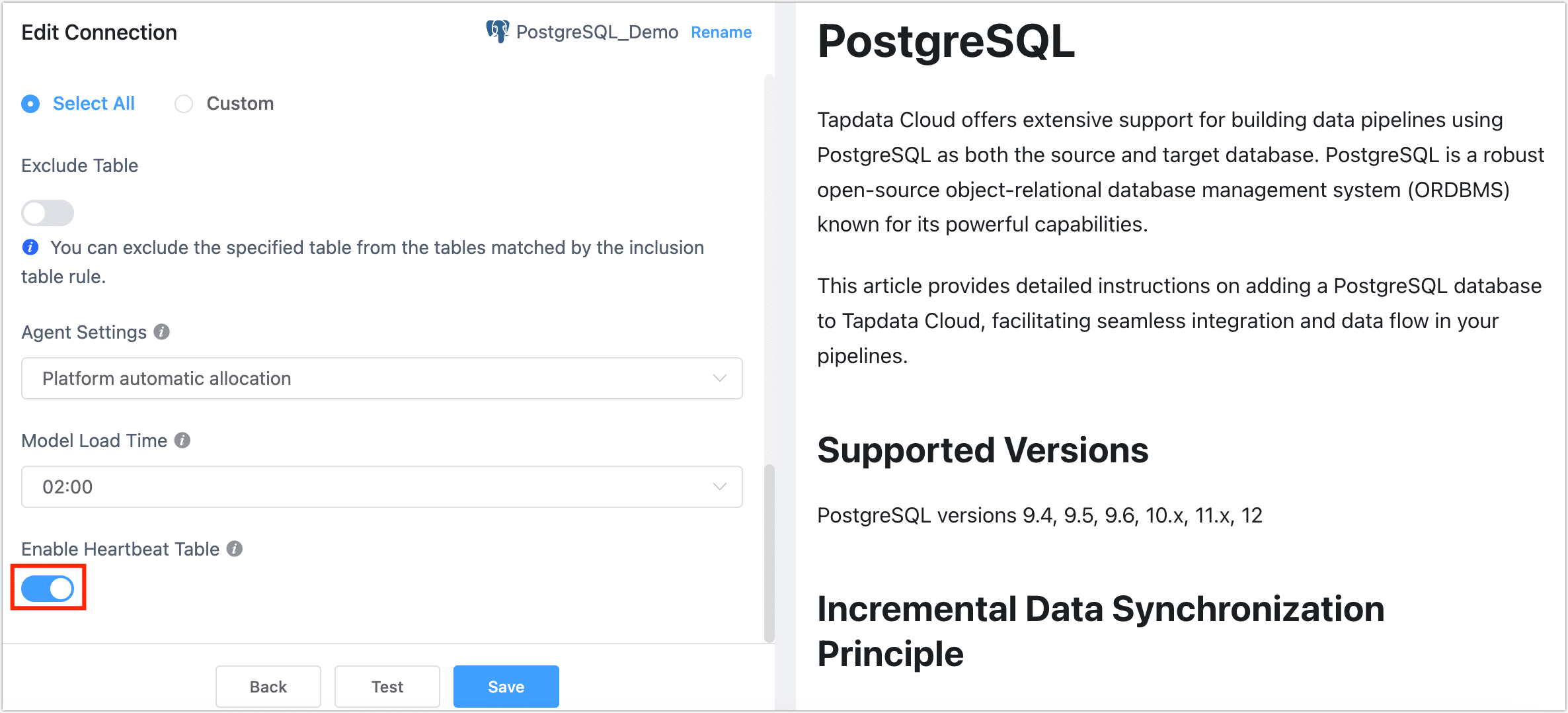 tip
tipIf you do not see this switch, check the Connection Type setting on the page to ensure it is set to Source and Target. Additionally, some data sources do not support being used as both source and target. For more information, see Supported Data Sources.
Click Save.
Viewing Heartbeat Table Tasks
Once the heartbeat table is enabled for a data source, the heartbeat task will start only after the data source is referenced and started in a data replication/development task. At this point, you can re-enter the edit page for that data source and click View Heartbeat Task.
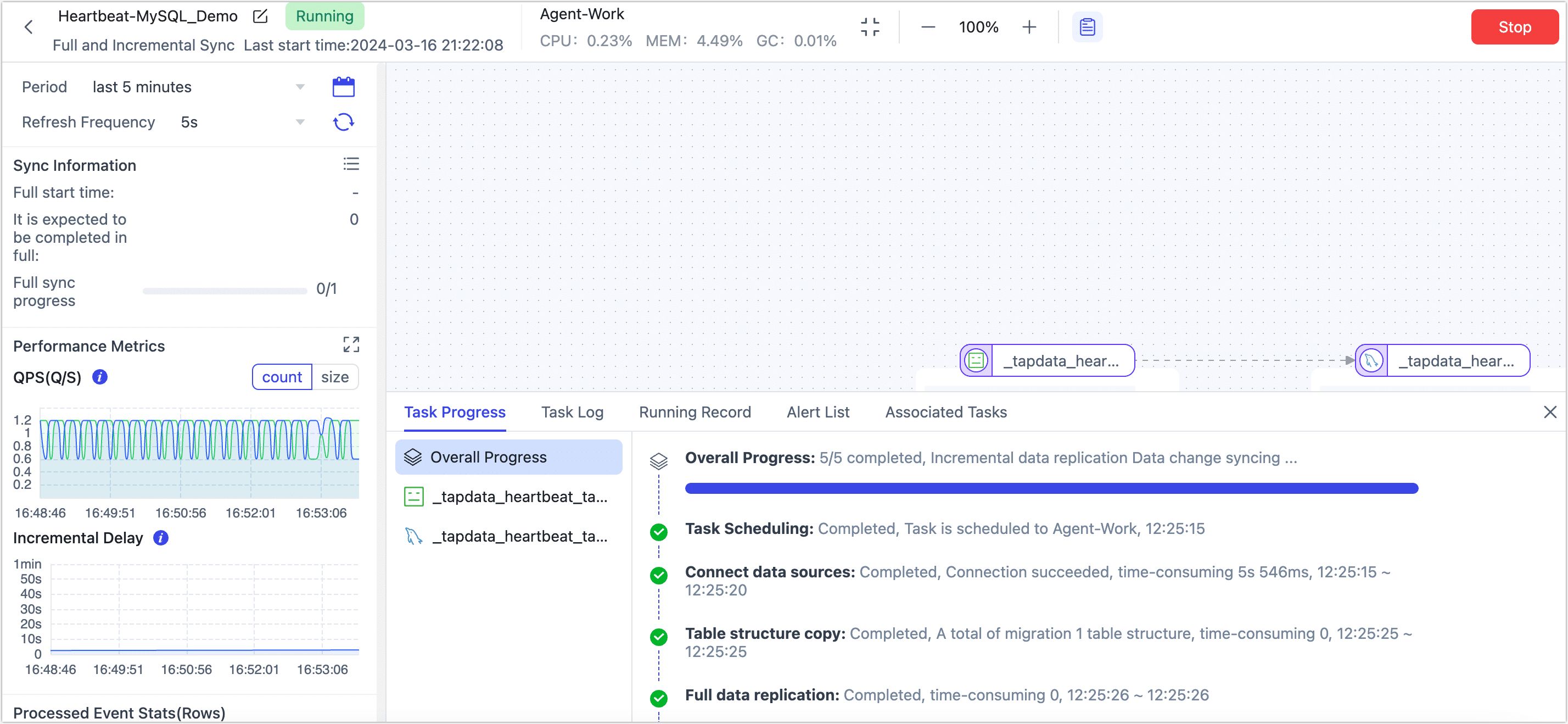
As shown above, TapData uses a Dummy data source to write a timestamp to the source database every 10 seconds, thus continuously updating the incremental checkpoint and better monitoring the data source and link status.
Common Questions
Q: Can I delete or edit the heartbeat table task?
A: No, you do not need to manually operate it. The heartbeat table task will automatically stop once all tasks associated with that data source are stopped. If that data source is deleted, the heartbeat task will also be automatically deleted.
Q: What are the structure and data contents of the heartbeat table?
A: For example, in MySQL, the table structure and data are as follows:
-- View heartbeat table structure
DESC _tapdata_heartbeat_table;
-- Result
+-------+-------------+------+-----+--------------------------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-------+-------------+------+-----+--------------------------+-------+
| id | varchar(64) | NO | PRI | 641a726eb1837461c70caa9d | |
| ts | datetime(6) | YES | | NULL | |
+-------+-------------+------+-----+--------------------------+-------+
-- View heartbeat table data
SELECT * FROM _tapdata_heartbeat_table;
-- Result
+--------------------------+----------------------------+
| id | ts |
+--------------------------+----------------------------+
| 6438cdbef713082e37eb0a05 | 2023-04-14 04:03:28.963000 |
+--------------------------+----------------------------+